Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
12.3.10.9.3. Signal correlation#
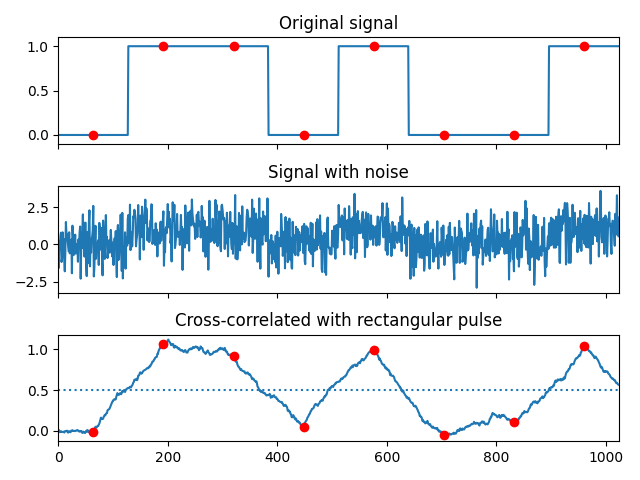
Implement a matched filter using cross-correlation, to recover a signal that has passed through a noisy channel.
from scipy import signal
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sig = np.repeat([0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0], 128)
sig_noise = sig + np.random.randn(len(sig))
corr = signal.correlate(sig_noise, np.ones(128), mode="same") / 128
clock = np.arange(64, len(sig), 128)
fig, (ax_orig, ax_noise, ax_corr) = plt.subplots(3, 1, sharex=True)
ax_orig.plot(sig)
ax_orig.plot(clock, sig[clock], "ro")
ax_orig.set_title("Original signal")
ax_noise.plot(sig_noise)
ax_noise.set_title("Signal with noise")
ax_corr.plot(corr)
ax_corr.plot(clock, corr[clock], "ro")
ax_corr.axhline(0.5, ls=":")
ax_corr.set_title("Cross-correlated with rectangular pulse")
ax_orig.margins(0, 0.1)
fig.tight_layout()
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.232 seconds)
