Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
12.1.10.5.5. Datetime#
This demo shows how the x-axis of a 1d plot can be a date time.
import numpy as np
import datetime
from itom import dataObject
from itom import plot1
Start date with a specific timezone.
timestamp = datetime.datetime(
2022, 5, 6, 12, 23, 5, tzinfo=datetime.timezone(datetime.timedelta(0, -7200))
)
Create a list of datetime.datetime objects.
numsteps = 100
dateList = []
for x in range(0, numsteps, 15):
dateList.append(timestamp + datetime.timedelta(hours=x))
Create a dataObject from the list of datetime objects.
dateScale = dataObject([1, len(dateList)], "datetime", data=dateList)
values = dataObject.randN(dateScale.shape, "float32")
[i, h] = plot1(values, dateScale)
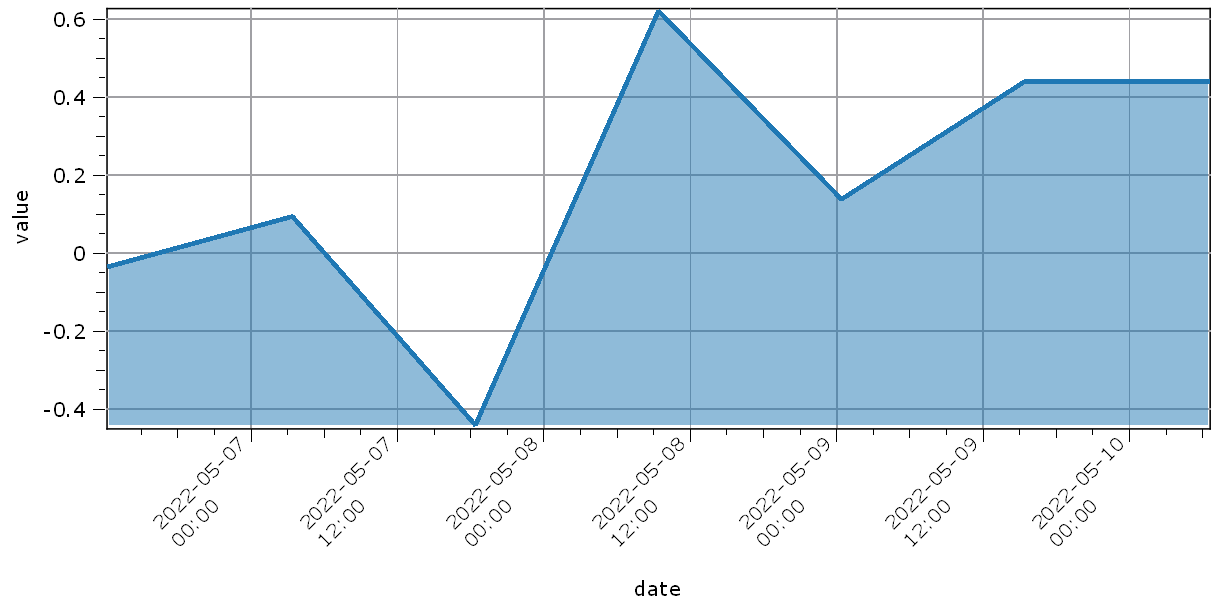
h["lineWidth"] = 3
h["axisLabelRotation"] = -45
h["axisLabelAlignment"] = "AlignLeft"
h["fillCurve"] = "FillFromBottom"
h["grid"] = "GridMajorXY"
h["axisLabel"] = "date"
h["valueLabel"] = "value"
Example with numpy datetime array.
dateScale2 = np.arange("2005-02", "2005-03", dtype="datetime64[D]")
values2 = dataObject.randN([1, len(dateScale)], "uint8")
plot1(values2, dateScale2)
(124, PlotItem(UiItem(class: Itom1DQwtPlot, name: plot0x0)))
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.137 seconds)
